As accountants identify the mistakes, they rectify the same in the worksheet to ensure debits are equal to credits. A bookkeeper or accountant keeps track and records all financial accounting activities for that particular financial year. Companies or businesses repeat the process every financial year to monitor, assess, and understand the real financial scenario. The accounting period for this assessment can be monthly, quarterly, annual, or any specific time range. For example, when a transaction is recorded using accrual accounting, it happens at the time of the sale.
- All public companies that do business in the U.S. are required to file registration statements, periodic reports, and other forms to the U.S.
- A budget cycle can use past accounting statements to help forecast revenues and expenses.
- Real or permanent accounts, i.e. balance sheet accounts, are not closed.
- There are several different amounts of time that a company may choose to report on.
- If you don’t track your transactions accurately, you won’t be able to create a clear accounting picture.
Identifying and recording transactions.
You can also link your ERP and other systems so the accounting software can record and monitor expenses. Accounting software can help avoid the hassle of correcting these errors because it checks the amounts and whether debits and credits are equal when you post journal entries. Gift cards are a great way for a company to presell its products and to create cash flow. One of the problems with gift cards garmin fenix 5 is that fraudsters are using the retailer’s weak internal controls to defraud the retailer’s customers. A fraudster can hack into autoloading gift cards and drain a customer’s bank account by buying new, physical gift cards through the autoloading gift card account. Accountants can help their organization limit gift card fraud by reviewing their company’s internal controls over the gift card process.
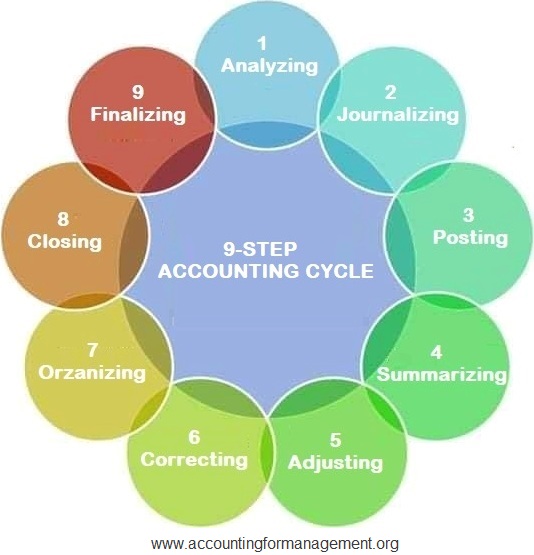
Steps in the Accounting Cycle
In addition, bookkeepers in companies use accounting software solutions to ensure the utmost accuracy of the process. The accounting cycle deals with creating different financial statements that companies go through at the end of each financial year to assess their current market position. The process starts with accounting transactions and ends with the closure of the books of accounts.
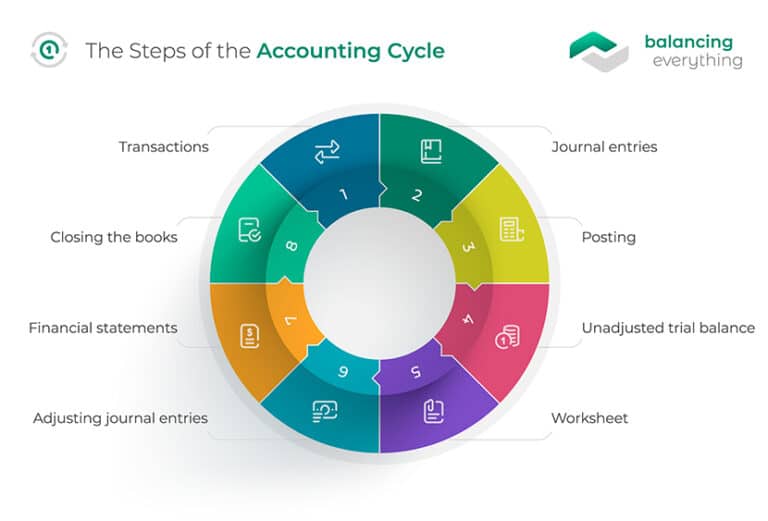
Step 2: Post transactions to the ledger
After the unadjusted trial balance has been calculated, the worksheet can be analyzed. Worksheets allow bookkeepers to identify adjusting entries so that the accounts are balanced. This step is also where bookkeepers will ensure that debits and credits are equal. This step also allows businesses that use accrual accounting to adjust for revenue and expenses. The accounting cycle is a series of steps starting with recording business transactions and leading up to the preparation of financial statements. This financial process demonstrates the purpose of financial accounting–to create useful financial information in the form of general-purpose financial statements.
Step 5: Analyze a Worksheet / Reconcile Accounts
This happens regardless of whether or not cash has moved in or out of business. It creates a debit for where the money is going, and a credit for where it is ending up. When the accounts are already up-to-date and equality between the debits and credits have been tested, the financial statements can now be prepared. The financial statements are the end-products of an accounting system. A trial balance is prepared to test the equality of the debits and credits. All account balances are extracted from the ledger and arranged in one report.
At the end of any accounting period, a trial balance is calculated for all accounts on the general ledger. This trial balance tells the company the amount of cash each unadjusted account is worth. Calculating these balances is crucial, as they are used for testing and analysis.
The better prepared your staff is, the more efficient they can be. As a business, we need to generate revenue to sustain our content. We have financial relationships with some companies we cover, earning commissions when readers purchase from our partners or share information about their needs.
A typical accounting cycle is a 9-step process, starting with transaction analysis and ending with the preparation of the post-closing trial balance. The fundamental concepts above will enable you to construct an income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement, which are the most important steps in the accounting cycle. To learn more, check out CFI’s free Accounting Fundamentals Course. This is a crucial step when you find that your trial balance’s debits and credits aren’t equal. To locate the error, compare the information in question to previous journal entries on the spreadsheet. The exact steps of the accounting cycle may vary according to a company’s unique needs.

